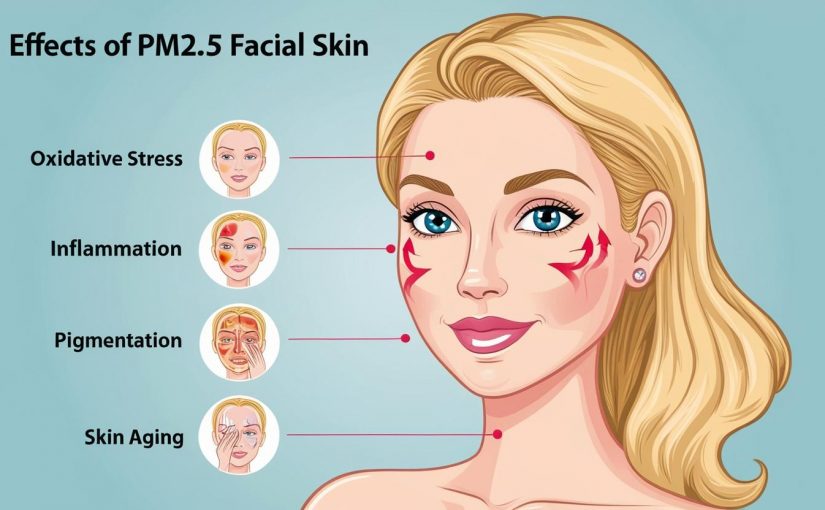
Recent studies have highlighted the harmful effects of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on human skin. PM2.5, a major component of air pollution, has been linked to skin aging, pigmentation changes, and inflammatory skin conditions. Researchers have explored its role in hyperpigmentation and oxidative stress-related skin damage.
PM2.5 and Hyperpigmentation
A study using a reconstructed human epidermis model demonstrated that exposure to PM2.5 can stimulate melanin production, leading to skin darkening. The research revealed that PM2.5 activates melanocytes indirectly through keratinocyte signaling pathways, leading to increased melanin synthesis. Additionally, toxic compounds such as benzo[a]pyrene (BAP) present in PM2.5 contribute to this effect by triggering oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.
Mechanisms of Skin Damage
PM2.5 exerts its harmful effects primarily through:
- Oxidative stress: It generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to cellular damage and inflammation.
- Inflammatory response: Exposure triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating skin conditions.
- Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation: PM2.5 contains polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which bind to AhR in skin cells, influencing melanin production and skin barrier integrity.
Health Implications and Prevention
Understanding the effects of PM2.5 on the skin emphasizes the need for protective measures, including:
- Using antioxidants: Skincare products containing vitamins C and E, and polyphenols form natural extracts can help neutralize oxidative stress.
- Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen: UV exposure enhances the negative effects of PM2.5 on pigmentation.
- Cleansing routines: Proper skin cleansing can remove pollutants and minimize their impact.
- Air quality awareness: Avoiding outdoor activities during high pollution days and using air purifiers can reduce exposure.
Treatment Options for PM2.5-Induced Skin Pigmentation
To combat the effects of PM2.5 on skin pigmentation, a combination of advanced dermatological treatments and supportive skincare approaches can be beneficial. Here are some recommended treatment options:
1. Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser for Pigment Correction
Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser is an effective treatment for reducing hyperpigmentation caused by environmental pollutants like PM2.5. This laser technology targets melanin deposits, breaking them down for natural elimination by the body.
For optimal safety and efficacy:
- It is recommended to use a USFDA-approved device.
- The procedure should be performed by a qualified and experienced dermatologist to minimize side effects and ensure desired results.
2. Multivitamin Therapy with Natural Whitening Agents
Antioxidant-based skin therapy plays a crucial role in neutralizing oxidative stress induced by PM2.5 exposure. A combination of multivitamins and natural skin-brightening agents can help:
- Reduce oxidative damage from free radicals.
- Enhance skin repair and collagen production.
- Support melanin balance to prevent excessive pigmentation.
- Key ingredients may include Vitamin C and natural extracts known for their depigmenting properties.
3. BioGlow Rejuvenation: Advanced Skin Revitalization
BioGlow Rejuvenation is a comprehensive facial treatment designed to brighten skin tone, reduce pigmentation, and enhance skin renewal. This treatment combines:
- Laser brightening to target melanin irregularities.
- Pigmentation reduction through vitamin and natural whitening treatment.
- Stem cell rejuvenation to repair and restore skin affected by environmental stressors.
Conclusion
PM2.5 exposure contributes to skin pigmentation, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Protecting the skin with antioxidants, proper cleansing, and sun protection can help minimize damage. For treatment, Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser, multivitamin therapy, and BioGlow Rejuvenation offer effective solutions to restore skin health and brightness.